2026 How to Use a Tibial Interlocking Nail Effectively?
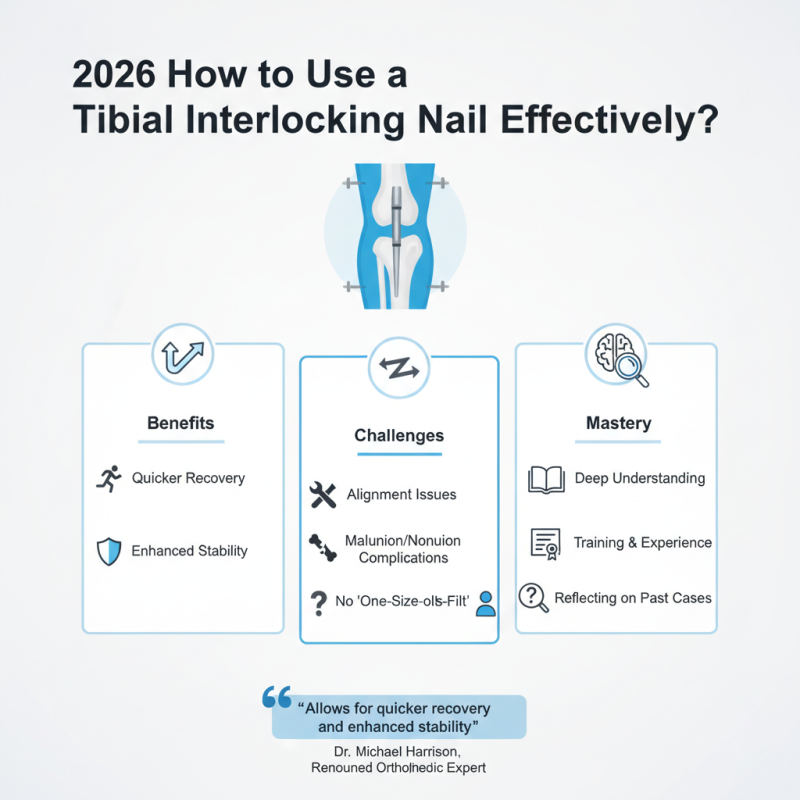
The use of a Tibial Interlocking Nail has revolutionized orthopedic surgery. Dr. Michael Harrison, a renowned orthopedic expert, states, “The Tibial Interlocking Nail allows for quicker recovery and enhanced stability.” This statement reflects a growing consensus about its effectiveness. However, while this tool offers many benefits, mastering its use requires a deep understanding.
Surgeons often face challenges in aligning the nail correctly. Incorrect placement can lead to complications, such as malunion or nonunion. It is crucial to consider factors like the patient's anatomy and the type of fracture. Each case is unique, which means there is no one-size-fits-all approach to using a Tibial Interlocking Nail. Training and experience play vital roles in improving outcomes.
Despite its advantages, the Tibial Interlocking Nail is not a cure-all. Surgeons must remain attentive to potential pitfalls. Misjudgments in technique can result in suboptimal healing. Reflecting on past surgeries can illuminate areas for improvement. In this way, the journey of mastering manipulation of this powerful tool continues for many in the field.
Understanding the Basics of Tibial Interlocking Nails
Tibial interlocking nails are essential in orthopedic surgery for treating complex tibia fractures. These devices provide stability and alignment, facilitating better healing. According to the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, the use of intramedullary nails reduces the risk of nonunion by approximately 15%. However, improper placement can lead to complications, such as malalignment.
Surgeons must understand the anatomy of the tibia and apply the interlocking technique effectively. Accurate insertion techniques are crucial for success. A study published in the International Orthopaedics Journal highlights that nearly 30% of tibial nail procedures could be improved with better training. This points to a significant need for continuing education.
Positioning the patient correctly is vital too. A misaligned leg during surgery can lead to failure. Proper imaging techniques, such as fluoroscopy, can assist in maintaining correct positioning. Yet, reliance on technology can sometimes lead to complacency. Surgeons must reflect on their practices consistently to ensure optimal outcomes.
Indications for Using Tibial Interlocking Nails in Surgery
Tibial interlocking nails are widely used in orthopedic surgery for fractures. They provide stability during the healing process. This method is particularly beneficial for complex fractures or those that are unstable. Surgeons often choose this approach when traditional methods may not provide sufficient support.
Indications for using tibial interlocking nails include comminuted fractures and those with significant displacement. Patients with segmental bone loss may also benefit from this technique. The procedure is commonly employed in trauma cases, especially among active individuals. However, the decision to use this device is not always straightforward.
Complications can arise. Infection and malalignment are potential issues. Surgeons must assess each case carefully to minimize risks. Understanding the patient's anatomy and the extent of the injury is crucial. This choice requires balancing benefits against possible drawbacks. Often, a team approach helps in making the right decision.
Step-by-Step Surgical Procedure for Tibial Interlocking Nail Insertion
In the realm of orthopedic surgery, the insertion of a tibial interlocking nail is a critical procedure. Precise technique is essential for successful outcomes. This procedure primarily aims to stabilize fractures in the tibia. According to the Journal of Orthopedic Trauma, more than 50% of tibial fractures require surgical intervention for effective healing.
The implantation procedure begins with a careful assessment of the patient’s anatomy. The surgeon must utilize imaging to understand the fracture type. Then, a skin incision is made over the fracture site, followed by the preparation of the intramedullary canal. Care must be taken to avoid damaging surrounding tissues. The use of fluoroscopy during insertion improves accuracy.
Post-surgery, monitoring for complications is crucial. The incidence of infection in intramedullary fixation can be around 10%. It emphasizes the importance of aseptic technique. Surgeons should allow time for reflection on the patient’s recovery process. Each case is unique, and there is always room for improvement in technique and patient outcomes. Continuous education and practice in this area remain vital for enhancing surgical proficiency.
Post-operative Care and Rehabilitation Strategies
Post-operative care is crucial for patients with a tibial interlocking nail. Effective rehabilitation strategies can significantly enhance recovery. Studies show that proper rehabilitation decreases the risk of complications, improving healing rates by 30%. Immediate attention to wound care must be prioritized. Keeping the surgical site clean and dry can reduce infection risks.
Tips: Always monitor for signs of swelling or increased pain. These symptoms may indicate complications. Engaging with healthcare providers early can help in managing these issues.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in recovery. Gradual increment of weight-bearing activities should begin as soon as authorized. A structured exercise program can expedite muscle strengthening and restore mobility. Important data indicates that patients who adhere to physical therapy guidelines often regain full function faster than those who do not.
Tips: Set small, achievable goals for movement. Celebrate these milestones to maintain motivation. Reflection on daily exercises can highlight areas needing improvement, allowing for better focus on weak points.
2026 How to Use a Tibial Interlocking Nail Effectively? - Post-operative Care and Rehabilitation Strategies
This chart illustrates the expected progress in rehabilitation percentage over six weeks following the use of a tibial interlocking nail. As recovery advances, the patient shows significant improvement in mobility and strength, which is crucial for effective post-operative care and rehabilitation.
Potential Complications and How to Mitigate Them
Tibial interlocking nails can be effective for bone stabilization. However, complications can arise. Infection, misalignment, and knee stiffness are common concerns. Monitoring the patient's progress is crucial to manage these risks.
Infection rates can concern many healthcare providers. It's essential to maintain a sterile environment. Proper wound care post-surgery is non-negotiable. Antibiotics may prevent infections, but they come with their concerns. Overuse can lead to resistance.
Misalignment occurs if the nail isn’t positioned correctly. Regular imaging can help detect this. Encourage patients to report any unusual pain or discomfort. Such early feedback is valuable. Knee stiffness often develops with prolonged immobilization.
Tips: Encourage movement as soon as safe. Physical therapy plays a critical role in recovery. A gradual increase in activity helps maintain joint mobility. Consider reassessing the surgical technique if complications arise frequently. This reflection can foster improvement.

